Table of Contents
Introduction
The upper back is part of the thoracic region of the spine, surrounded by various muscles that protect the thoracic joints and help assist with respiratory functionality for the lungs. The upper back muscles consist of the rhomboids and the trapezoid muscles that provide functionality to the scapula or shoulder blades. Other superficial muscles offer assistance to the thoracic spine. The serratus posterior muscle is one of the superficial muscles that helps the thoracic spine and, like all superficial muscles, can succumb to injuries that can lead to the development of overlapping referred pain symptoms known as trigger points. Today’s article focuses on the serratus posterior muscle function in the back, how trigger points are causing upper back pain, and various techniques to manage trigger points in the upper back. We refer patients to certified providers who are diverse in upper back pain therapies to aid many people suffering from myofascial pain syndrome or trigger points associated with the serratus posterior muscle along the upper back. We advised patients by referring them to our associated medical providers based on their examination when appropriate. We indicate that education is a great solution to asking our providers profound and complex questions at the patient’s request. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., notes this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
The Serratus Posterior Muscle Function In The Back
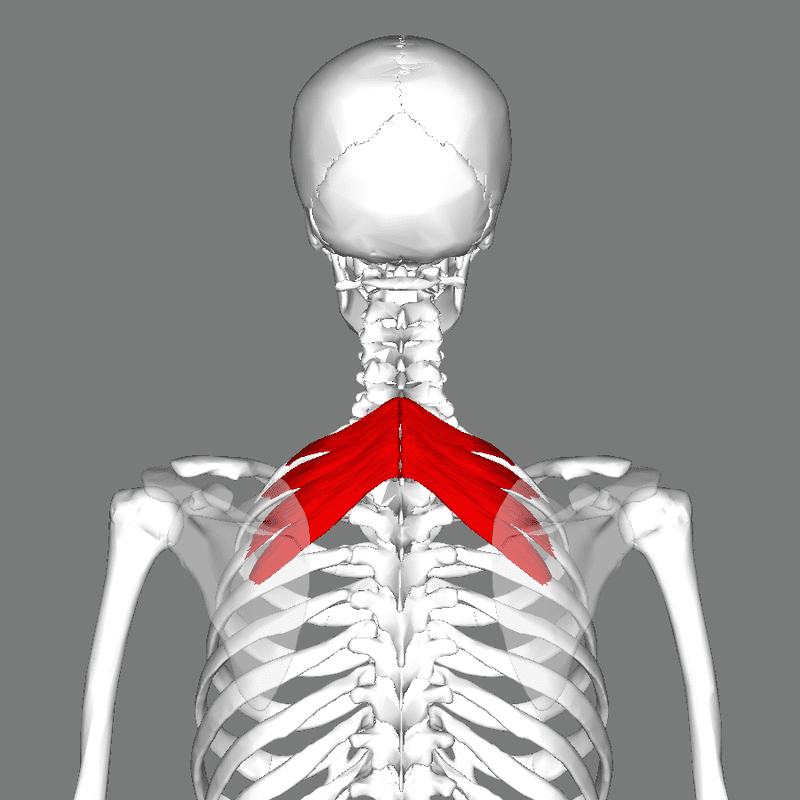
Have you been dealing with constant upper back pain? Do you feel soreness at the base of your neck? Or are you having difficulty breathing? Most of the symptoms cause pain in the serratus posterior muscles that can lead to the development of myofascial pain syndrome or trigger points along the upper back. The serratus posterior has various roles in the upper back as it is not only part of the extrinsic muscles but also part of the accessory breathing muscle. The serratus posterior muscle helps with inspiration, which causes the chest cavity to expand as it is a superficial muscle attached to the ribs and is less commonly known. Studies show that the serratus posterior muscle is deep within the rhomboid muscles and is superficial. Even though this muscle is superficial when it has been overused through various activities, that can cause hypertrophy in the accessory respiratory muscles. Additional studies reveal that the serratus posterior superior muscle is considered clinically insignificant but has been impaired by myofascial pain syndrome or trigger points that can lead to upper back pain.
Trigger Points Causing Upper Back Pain
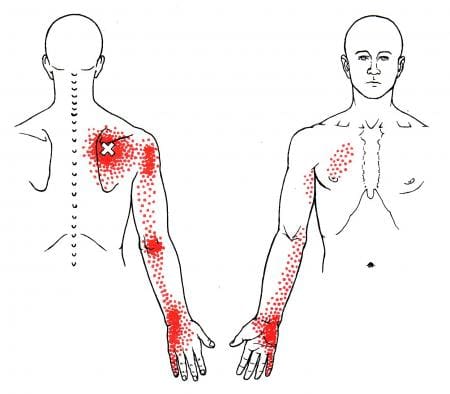
As stated earlier, the upper back is part of the thoracic region of the spine, and when various factors begin to affect the body, the back muscles tend to be involved. Studies reveal numerous sources of spinal pain in the thoracic spine. One is a myofascial pain syndrome affecting the serratus posterior muscles causing referred upper back pain. Myofascial pain syndrome or trigger points can be activated when the serratus posterior muscle is overloaded from thoracic respiratory issues like coughing due to pneumonia, asthma, or chronic emphysema. When respiratory problems affect the muscles in the thoracic region of the back, it leads to the development of trigger points, leading to overlapping issues like referred pain, motor dysfunction, and autonomic phenomena. According to Dr. Travell, M.D., in the upper back, trigger points can make the serratus posterior muscle cause overlapping risk profiles along the shoulder blades and have referred pain travel to the hands. This can make many individuals suffer from serious pain-like symptoms, causing them to be miserable.
Releasing Trigger Points Related Tension In The Upper Back-Video
Have you been dealing with respiratory issues causing you to be hunched over constantly? Do you feel soreness or tenderness at the base of your neck? Or are you suffering from upper back pain? These symptoms are associated with trigger points that are affecting the serratus posterior muscles causing upper back pain. Trigger points, or myofascial pain syndrome, is a musculoskeletal disorder that causes tenderness along the affected muscle that causes referred pain to the surrounding muscles in the body. Trigger points associated with the serratus posterior muscles can cause referred pain in the upper back and mimic various chronic conditions. Trigger point pain is difficult to diagnose but can be manageable with treatment. The video above gives examples of how to treat trigger points to relieve tension in the upper back.
Various Techniques To Manage Trigger Points In The Upper Back
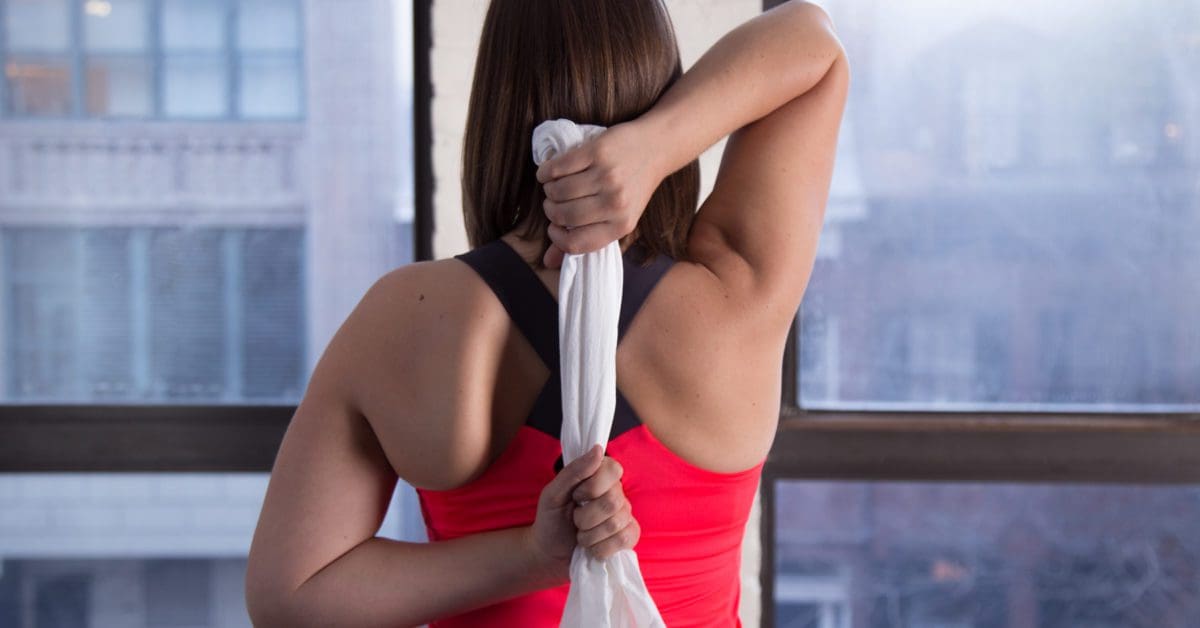

When it comes to upper back pain, many individuals will go to pain specialists like massage therapists or chiropractors to relieve any issues affecting the upper back. These pain specialists utilize various techniques like stretching, spinal manipulation, massages, and ischemic compression to alleviate pain and manage trigger points from forming further in the affected muscle. Pain specialists like massage therapists or chiropractors are excellent for locating pain-like symptoms associated with trigger points. Even though treatment can help manage symptoms associated with trigger points, many people can still incorporate these techniques, like deep breathing or correcting their posture, to prevent the upper back muscles from becoming strained and causing more issues than before.
Conclusion
The serratus posterior muscles have various roles in the upper back region of the body. These superficial muscles are extrinsic and accessory breathing muscles that help expand the chest cavity. When multiple issues affect the upper back muscles, like strenuous activities or respiratory problems, it can develop trigger points along the serratus posterior muscles and invoke pain-like symptoms to travel down to the hand, causing mobility issues. Thankfully, various techniques that pain specialists like chiropractors and massage therapists use can help manage trigger points from escalating and can bring upper back mobility to the body once again.
References
Altafulla, Juan J, et al. “An Unusual Back Muscle Identified Bilaterally: Case Report.” Cureus, Cureus, 15 June 2018, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6093753/.
Briggs, Andrew M, et al. “Thoracic Spine Pain in the General Population: Prevalence, Incidence and Associated Factors in Children, Adolescents and Adults. A Systematic Review.” BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, BioMed Central, 29 June 2009, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2720379/.
Mitchell, Brittney, et al. “Anatomy, Back, Extrinsic Muscles.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 4 Aug. 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537216/.
Travell, J. G., et al. Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual: Vol. 1:Upper Half of Body. Williams & Wilkins, 1999.
Vilensky, J A, et al. “Serratus Posterior Muscles: Anatomy, Clinical Relevance, and Function.” Clinical Anatomy (New York, N.Y.), U.S. National Library of Medicine, July 2001, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11424195/.
Disclaimer
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card


