I have been travelling through Athens and now Istanbul. My 11 year old is a Percy Jackson nut and has been filling me in with the who’s who of Greek mythology and I am learning Latin words every day. Quite an education!
I looked up the word syndesmosis and the Latin translation is “(New Latin, from Greek sundesmos) bond, ligament, from sundein, meaning to bind together”. As sports injury professionals, we know syndesmosis to be the joint articulation between the tibia and the fibula bones around the ankle. These two bones are ‘bound’ together with very firm and strong ligaments.
Syndesmosis comes to mind after I saw a girl sprain a syndesmosis at the Archaeological Museum in Istanbul today. This poor girl was preoccupied by the hundreds of cats and kittens running all over the place and did not see the uneven cobblestones on which she placed her foot. At the same time, she turned to change direction. This is a common mechanism of injury for a syndesmosis – a forced dorsiflexion and rotation on a fixed foot.
Table of Contents
Rehab Masterclass Issue 140 Of Sports Injury Bulletin
Of all the ankle injuries, injury to the syndesmosis is the biggest pest to sports physios and the like. And unlike simple garden variety ankle sprains that heal quickly, the syndesmosis takes a LONG time to heal properly. If you deal with athletes that are susceptible to syndesmosis sprains, I’m sure you will agree that these are harder injuries to manage because of the severe consequences if done badly.
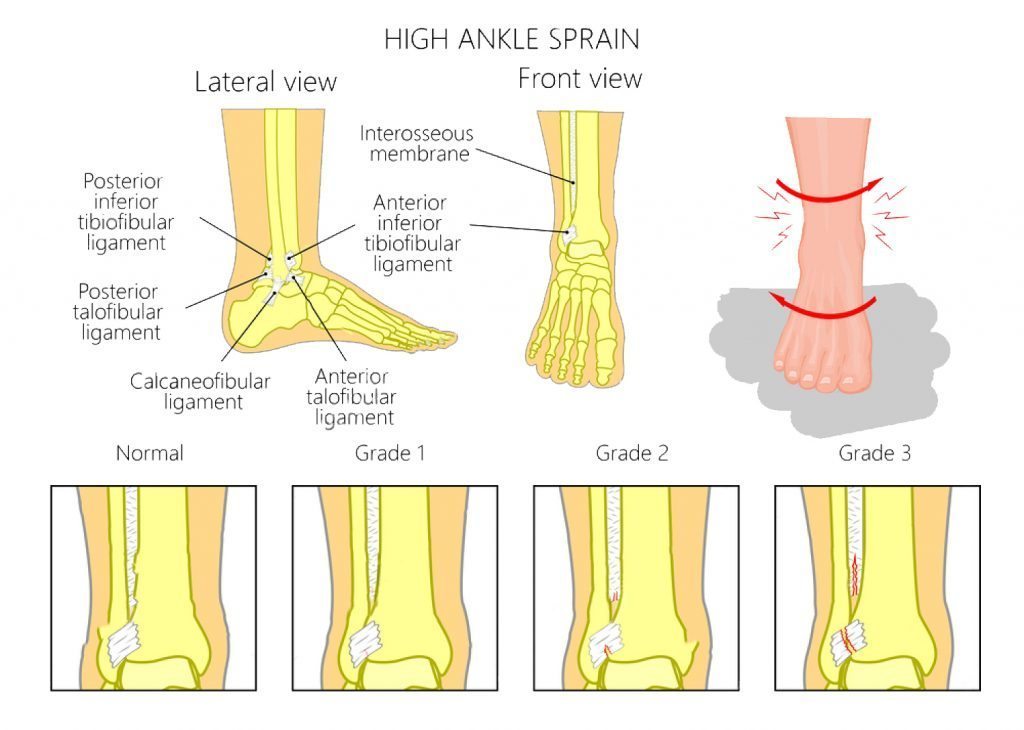
I go into a fair bit of detail in my Sports Injury Bulletin piece about syndesmosis injuries, detailing how they happen, how to identify them and then manage them. What I would like to highlight here are the implications of mismanaging a syndesmosis sprain.
In the current issue of The Journal of Sports and Physical Therapy, a group of Japanese researchers discovered that individuals who had chronic ankle instability (CAI) had a distal fibula that was positioned more lateral compared with healthy individuals with no CAI. In effect, those who had suffered serious syndesmosis injuries in the past and ended up with a wider distance between the fibula and the tibia, suffered more ongoing ankle pain than those without a tibfib separation.
Research shows that even a 1mm displacement of the talus within the mortise (due to a wider placed fibula) can reduce the contact area in the talocrural joint by 42% (Ramsey and Hamilton 1976). Mismanaged syndesmosis injuries, resulting in an excessive amount of opening, can lead to early onset arthritic changes and chronic ankle instability. The talus bone bounces around in the now wider tibfib articulation.
A Widening Of The Fibula Is Due To One Of The Following:
Poor initial management, whereby the athlete is allowed to weight bear too early and this weight bearing forces the fibula away from the tibia as the syndesmosis ligaments are trying to heal.
The degree of damage is so severe that proper tightening of these ligaments is not possible without surgical intervention such as a screw or similar being placed between the two bones to ‘force’ them together.
The key for a sports injury practitioner, is to properly identify a regular ankle sprain from a more serious syndesmosis injury. If you get this part wrong and allow the athlete to get back to weight bearing too early, then expect some complaints about a chronically painful ankle some time down the track.

Kobayashi et al (2014). ‘Fibular malalignment in individuals with chronic ankle instability.’ JOPST. 44(11); pp 841-910.
Ramsey and Hamilton (1976). J Bone and J Surgery Am. 58(3); 356-357.
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information on this blog site is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Wellness and Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of chiropractic practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters and issues that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807
New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Texas & Multistate
Texas RN License # 1191402
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card



Comments are closed.