Table of Contents
Introduction
When the body sustains an injury, the immune system springs into action by going to the injured area and healing it through inflammation. Inflammation in the body is necessary when a person is injured and the affected area swells and becomes inflamed and begins to heal shortly. When someone is doing a treatment for their own wellbeing, their bodies can induce inflammation in order to start the healing process and begin to recover afterward. In this 2 part series, we will be taking a look at how inflammation can affect the body after a regenerative procedure and what anti-inflammatory foods are perfect for the body. Part 1 discussed what are the post-procedure protocols that a person should follow after their regenerative treatment. By referring patients to qualified and skilled providers that specialized in regenerative cellular therapy, we work with affiliated clinics and distributor organizations, both internationally and nationally with the services that we offer. We find that education is the key to asking valuable questions to our providers. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
Can my insurance cover it? Yes, in case you are uncertain here is the link to all the insurance providers we cover. If you have any questions, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900.
What Is Regenerative Medicine?
When the body sustains a severe injury, it can damage the body’s cells, tissues, and organs causing the healing process to slow down than usual. Research shows that regenerative medicine helps restore, replace and regenerate the body’s cells to their original state. Regenerative medicine can even help with the body’s natural healing process by boosting it up. There are many affiliated clinics and distributors that do regenerative medicine internationally to make sure that the body is functioning normally and that the body’s cellular structure is intact.
What To Do After Regenerative Medicine Treatment?
In part 1, it showed the post-procedure protocols that a person should do. It is very important that the individual should take it easy after any procedure that they went through. By resting and relaxing the body as much as possible, the treatment can begin to heal the body and inflammation can help the healing process as well. However, if the person starts to disrupt the healing process by increasing the inflammatory cells in the body through a change of eating habits and lifestyle, it can kill the HTCP (human cellular tissue products) that are injected into the body and that can develop into chronic illnesses over time.
Lowering Inflammation In The Body
Studies show that inflammation is part of the body’s natural defense that the immune system sends out when there are harmful pathogens in the body. Inflammation can come in two forms which are acute inflammation and chronic inflammation. Acute inflammation is short-term inflammation on the area that has a bit of swelling and is gone after a few hours. Chronic inflammation is long-term inflammation where inflammation can last for weeks and can develop into chronic illnesses over time. It is very important that the body should rest and relax to keep the inflammatory cells from processing to be chronic. Some of the ways that people can lower inflammation in the body are by eating anti-inflammatory food that is both nutritious and delicious.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
One of the previous articles showed what types of foods are beneficial for the body and that can help with inflammation. Anti-inflammatory foods are part of a very important diet that can help dampen the effects of prolonged inflammation in the body known as the anti-inflammatory diet. The anti-inflammatory diet is widely regarded as a healthy diet and even if it doesn’t help the person’s inflammatory conditions, it can actually help lower the chances of other conditions that the individual may have. Some of the anti-inflammatory food include:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Fish
- Herbs & Spices
Research shows that the beneficial properties that come from anti-inflammatory foods can help lower chronic inflammation through natural antioxidants and polyphenols that are in certain fruits and vegetables.
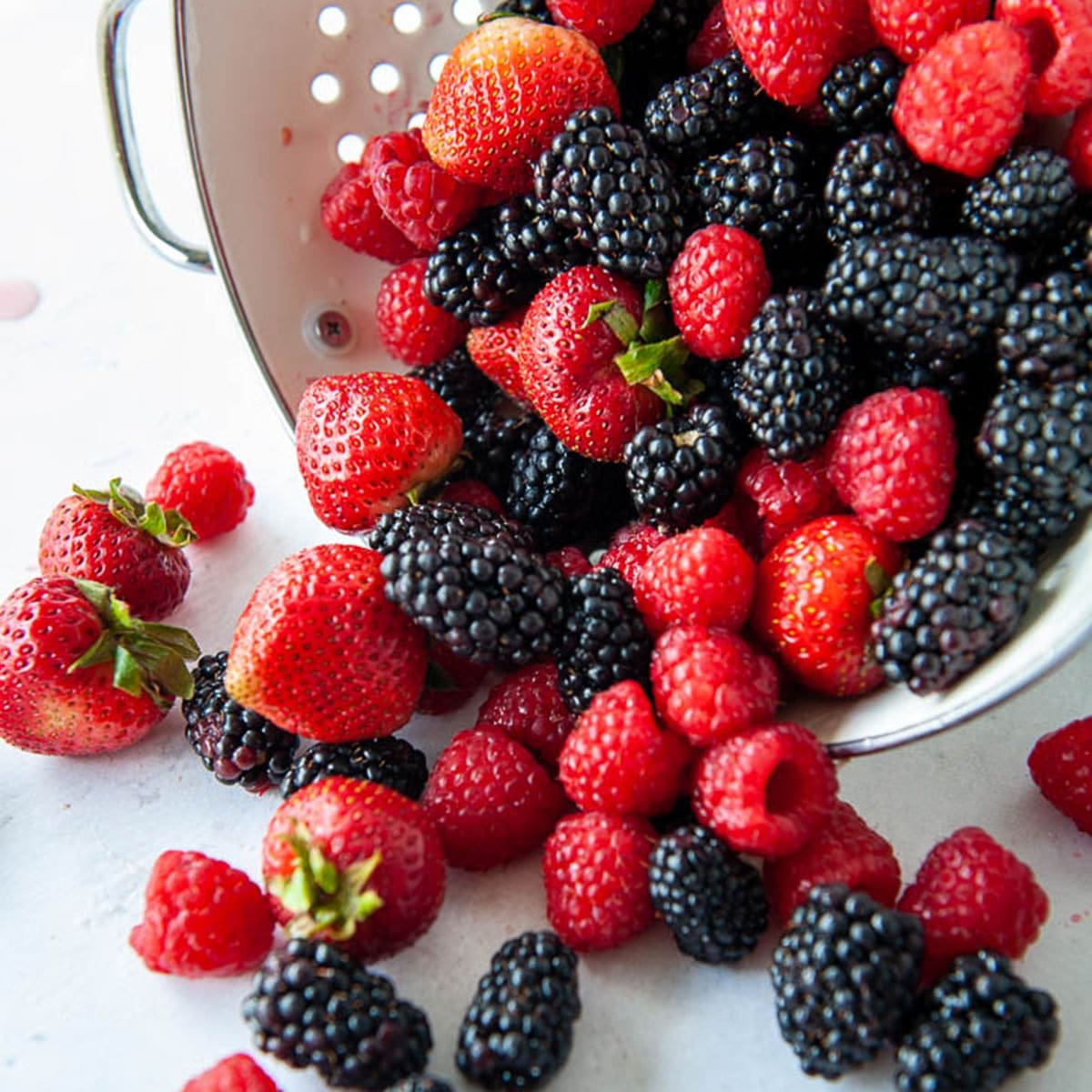
Fruits
Even though fruits are chaulked filled with the necessary vitamins and minerals that the body needs, it is also filled with antioxidants and can help lower the inflammatory cells from attacking the body when there are no harmful pathogens around. Research shows that berries are filled with antioxidants and the phytochemicals pigment can not only lower inflammation but can lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Vegetables
Just like fruits, many cruciferous vegetables like spinach, kale, and broccoli are filled with vitamin K and can help the body. All vegetables have the necessary nutrients and vitamins that the body needs and can be used in a variety of delicious dishes. Studies have shown that increasing the consumption amount of cruciferous vegetables not only helps lower inflammation but can also help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like cancer and cardiovascular diseases. The study also mentioned that eating cruciferous vegetables can also activate the body’s Nrf2 factors in the body.
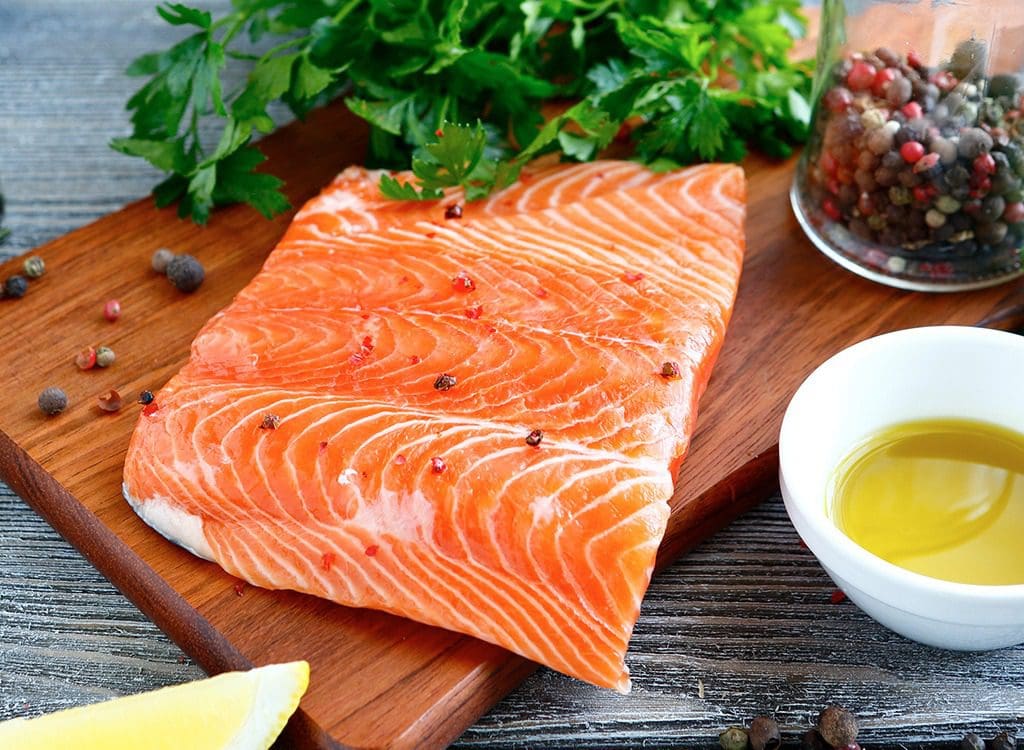
Fish
Fish are filled with omega-3 fatty acids that can be taken in vitamin form or through cooked fish can help lower the effects of inflammation in the body. Studies have found that omega-3 EFAs found in fish oil can reduce the effects of inflammatory responses to the body and reduce pain. Other studies have also proven that omega-3 fatty acids in fish can lower inflammatory chronic illnesses like IBD and rheumatoid arthritis and even neurodegenerative illness that the body has encountered.
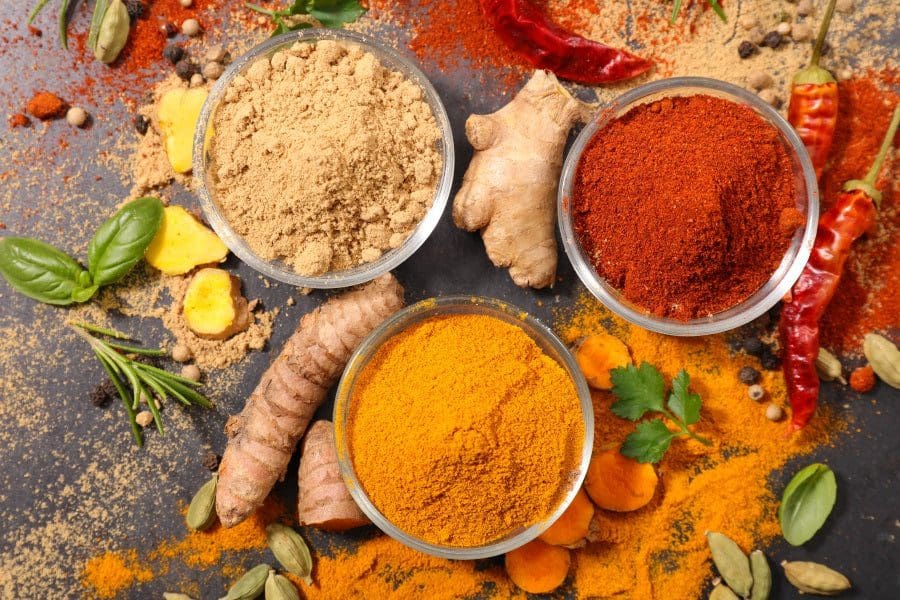
Herbs & Spices
Surprisingly there are many herbs and spices that can not only enhance the flavor of any delicious dish that someone creates but can help dampen the effects of inflammatory responses from hurting the body. Research shows that these herbs and spices have many potential health benefits that can boost cognitive function, reduce inflammation with their anti-inflammatory properties and even aid in the fight against cancer. One of the main spices that seem to be the most effective is turmeric. Turmeric can help lower inflammatory signals and even improve oxidative stress in the body. This spice has a high antioxidant content that can scavage toxic free radicals from the body with its antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties.
Conclusion
All in all, lowering inflammation is key when recovering from any kind of procedure. By following the protocols after the treatment and resting as much as the body can is key for the HCTP to do its job and make the body heal a bit faster. By incorporating healthy, nutritious food that can help lower inflammation is part of the recovery process. Without it and eating foods that can cause inflammation, will kill the HTCP treatment, and the body will suffer from prolonged inflammation over time. However, if a person follows the procedure correctly, changing their lifestyle habits, eating whole nutritious foods, and exercising regularly, then the body will heal faster and the individual can live life to the fullest.
References
Chen, Linlin, et al. “Inflammatory Responses and Inflammation-Associated Diseases in Organs.” Oncotarget, Impact Journals LLC, 14 Dec. 2017, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5805548.
Jessop, Zita M, et al. “Transforming Healthcare through Regenerative Medicine.” BMC Medicine, BioMed Central, 10 Aug. 2016, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4980802/.
Jiang, Yu, et al. “Cruciferous Vegetable Intake Is Inversely Correlated with Circulating Levels of Proinflammatory Markers in Women.” Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, U.S. National Library of Medicine, May 2014, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4063312/.
Maroon, Joseph Charles, and Jeffery W Bost. “Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Fish Oil) as an Anti-Inflammatory: An Alternative to Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs for Discogenic Pain.” Surgical Neurology, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Apr. 2006, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16531187/.
Martinez, Kevin. “Inflammation: Types, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment.” Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 13 Apr. 2020, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/248423.
Professionals, Harvard Health. “Foods That Fight Inflammation.” Harvard Health, 16 Nov. 2021, www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/foods-that-fight-inflammation.
Professionals, Havard Health. “Eat These Fruits for Their Anti-Inflammatory Benefits.” Harvard Health, 13 Oct. 2021, www.health.harvard.edu/nutrition/eat-these-fruits-for-their-anti-inflammatory-benefits.
Todd, Lindsey, and Sade Meeks. “10 Healthy Herbs and Spices: Anti-Inflammatory, Nutritious, and More.” Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 29 June 2021, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/healthy-herbs-and-spices.
Wall, Rebecca, et al. “Fatty Acids from Fish: The Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids.” Nutrition Reviews, U.S. National Library of Medicine, May 2010, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20500789/.
Disclaimer
Post Disclaimer
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Lowering Inflammation After Regenerative Post-Procedure | Part 2" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Our information scope is limited to Chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somatovisceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and/or functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.*
Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, RN*, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN*
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License # TX5807, New Mexico DC License # NM-DC2182
Licensed as a Registered Nurse (RN*) in Florida
Florida License RN License # RN9617241 (Control No. 3558029)
License Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Presently Matriculated: ICHS: MSN* FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, RN* CIFM*, IFMCP*, ATN*, CCST
My Digital Business Card